How to approach the benefits of the Natura 2000 network?
Project workers from the Global Change Research Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences – CzechGlobe, in cooperation with other partners, have developed and defined a conceptual framework that sets out a systematic and effective procedure for evaluating the sociocultural, economic and biophysical benefits of the Natura 2000 network.
The One Nature project focuses on evaluating the statuses of target features, ensuring practical measures in nature and long-term cooperation with owners and users of land located in protected areas. It also deals with presenting and, as a result, defending the benefits of valuable Natura 2000 network sites.
In order to have enough arguments and data on which specific biophysical, economic and socio-cultural benefits the protected areas provide, we have to evaluate them. However, this is conditioned by the fact that we all look at the given issue in a similar way and we understand each other’s bases of thought. This alignment of perspectives will facilitate the evaluation itself: the categorization of values, their qualitative and quantitative description. As a result, this process will bring outcomes that can be used, for example, to estimate the benefits coming from the production of individual ecosystem services or to evaluate the economic effects of the Natura 2000 network for local economic entities (e.g. benefits from tourism and recreation).
This is a very demanding process, especially in terms of time and expertise. This conceptual framework is inspired by the conceptual framework of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) and developed by a number of leading international experts. Our framework was developed to provide a common understanding of the socio-ecological system of the Natura 2000 network, to which the One Nature project is related, and the priority elements and links of this system at the same time.
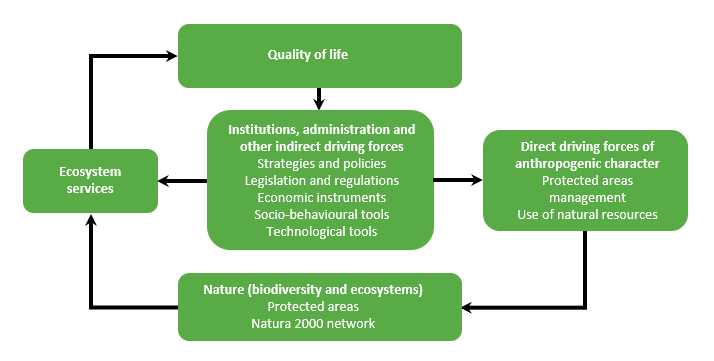
It also puts emphasis on the key role of institutions, administrations and other indirect drivers in the management of protected areas, the link between nature, ecosystem services and quality of life in the Natura 2000 network protected areas, and accentuates the different types of values associated with nature, ecosystem services and quality of life in Natura 2000 network sites.
-

- Scheme of the conceptual framework for the evaluation of socio-economic benefits of the Natura 2000 network (based on Díaz et al. 2015).
The basic element of the conceptual framework is the natural environment of the Czech Republic’s protected areas and the Natura 2000 network. Nature is associated with a number of intrinsic values, i.e. values independent of human use: biodiversity, individual organisms, biophysical systems and biophysical processes.
Natural ecosystems provide people with a number of benefits, so-called ecosystem services, such as the provision of food, materials, medicinal, biochemical and genetic resources. A list of all services defined for the One Nature project can be found on the Benefits of Protected Areas page.
The very values of nature will be assessed in terms of intrinsic and purposeful values as well as a relational value with regard to individual aspects of quality of human life, such as health and well-being, education and knowledge, good relations, security and livelihoods, governance and justice, diversity and accessible possibilities, sustainability and resilience, life in harmony with nature, identity and autonomy, spirituality and religiosity, art and cultural heritage.